Medical imaging is indispensable to modern healthcare. The images produced provide crucial insights into the human body’s structures and functions, ultimately allowing medical professionals to create better patient treatment plans. Through techniques like X-ray imaging, Computed Tomography (CT) scans, Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), and ultrasound, professionals can diagnose conditions ranging from fractures to tumors and even cancer.
The impact of medical imaging spans many specialties, improving patient management and survival rates. Within the diverse range of medical imaging trade career specializations, Radiography and Sonography are two of the most prominent.
Spot the Difference!
When considering a career in diagnostic medical imaging, it’s important to know how much you’ll earn, your work responsibilities, and your career growth prospects. Check out some of the key aspects of Radiography and Sonography through the table below:
| Radiography | Sonography | |
| Starting Salaries | $49,574 per year | $65,096 per year |
| Average Salaries | $83,453 annually | $84,410 annually |
| Career Growth | * Opportunities to specialize in areas like MRI or CT scanning * Promotion to supervisory or managerial positions | * Options to specialize in Obstetrics, Cardiovascular, or Musculoskeletal Sonography * Opportunities for career advancement into teaching or managerial positions |
| Work Environment | * Hospitals, clinics, imaging centers, or physician offices * Fast-paced with multiple patients * Exposure to radiation * Must follow strict safety protocols | * Medical facilities, outpatient centers, or private clinics * Procedures may take long, depending on the imaging requirement * Minimal exposure to radiation |
| Educational Path | * Associate degree or certificate program in Radiography * Licensing or certification required in most states | * Associate degree program in Sonography * Certification through organizations like ARDMS or ARRT |
| Job Outlook | Employment growth forecast of 6% from 2022 to 2032 | Expected job growth of 14.3% from 2022 to 2032 |
Getting to Know Radiography
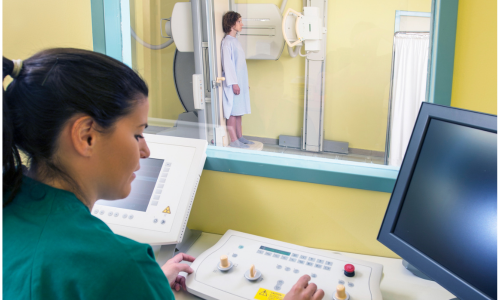
Radiography involves the use of radiation or X-rays that create images of the body’s internal structures. Capturing detailed images allows healthcare professionals to visualize certain parts of the human body. This mode of imaging plays a crucial role in diagnosing fractures, detecting organ abnormalities, finding foreign objects inside the body, and guiding surgical procedures.
Radiographers use a variety of instruments, such as X-ray machines, CT scanners, and fluoroscopy equipment, to capture high-quality images that help in patient diagnosis and treatment planning.
Becoming a Radiographer
Becoming a radiographer is an exciting journey that begins with specialized technical training or an associate degree program in Radiography, often offered by community colleges and technical schools. Radiography programs are designed to provide a comprehensive understanding of topics such as human anatomy, physiology, patient care techniques, radiation safety, and medical ethics.
Classroom instruction, laboratory exercises, and clinical rotations give you the foundational knowledge and practical experience needed to operate sophisticated imaging equipment.
You may also want to consider signing up for internships to develop your skills further and gain practical experience. Obtaining certification from medical institutions, like the American Registry of Radiologic Technologists (ARRT), may help you get an edge when looking for a job.
Focus on developing your soft skills. Communication, time management, and empathy are key! These skills are crucial when working with patients and healthcare professionals. Networking with industry professionals may also provide valuable opportunities for career advancement and mentorship.
Career Path for Aspiring Radiographers
If you’re passionate about healthcare and technology, radiography offers a fulfilling and dynamic career path with endless opportunities for learning and advancement. You’ll be prepared to pursue various jobs in hospitals, medical clinics, and other healthcare institutions. Some of the positions available are:
- Radiologic Technologist
- Mammography Technologist
- Radiation Therapist
- Quality Assurance Technologist
- Research Radiographer
- Radiology Administrator
Are You a Good Fit for Radiography?
The path to becoming a radiographer requires more than just technical proficiency. Successful radiographers possess a unique blend of characteristics that allow them to thrive in their roles.
A career in Radiography is for you if:
- Enjoys working with technology and medical equipment
- Thrives in fast-paced environments that interact with different patient
- Interested in anatomy and diagnostic imaging
- Prefers hands-on and practical work
A career in Radiography is not a great fit if:
- Uncomfortable with radiation exposure and safety protocols
- Prefers a career with less direct patient contact
- Not interested in continual learning and adapting to evolving imaging technologies
- Unable to work well under pressure or in emergencies
Getting to Know Sonography
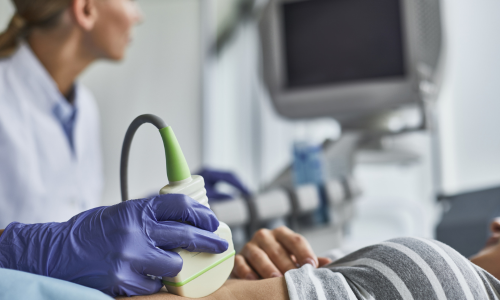
Commonly known as ultrasound imaging, Sonography uses sound waves to generate images and videos of the body’s internal organs and tissues. Sonography is non-invasive and does not involve radiation, making it a good choice for imaging during pregnancy.
This mode of imaging is also best used in treating abdominal conditions and detecting cardiovascular abnormalities. Sonographers often collaborate with medical professionals in interpreting diagnostic data and providing essential insights for patient care.
Becoming a Sonographer
Becoming a Sonographer typically involves completing a specialized training program or finishing an associate degree in diagnostic medical Sonography. These programs cover important topics, including anatomy, physiology, patient care, and ultrasound physics.
Specializations include ultrasound Physics, abdominal Sonography, Obstetric and Gynecologic Sonography, and Vascular Sonography, which all provide a strong foundation in Sonography while preparing you for the technical aspects of the profession. You may also gain practical experience through internships or clinical rotations, which helps in developing essential skills in patient interaction and medical technology.
Often required by employers, it’s best to get certification from recognized organizations: the American Registry of Radiologic Technologists (ARRT) and the American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonography (ARDMS). The specializations include Breast Sonography, Pediatric Cardiac Sonography, or Echocardiography.
Some of the skills needed to succeed in this field include proficiency in operating medical equipment, communication abilities to interact with patients and healthcare providers, and the ability to adapt to new technologies and procedures.
Career Path for Aspiring Sonographers
Being a sonographer is a fun and rewarding trade career! You’ll find that you can have a meaningful impact on patients’ lives by providing crucial diagnostic information. After graduating and obtaining certification, Sonographers can pursue different career opportunities in healthcare settings such as diagnostic imaging centers, physician offices, and outpatient clinics. Common job positions include:
- Diagnostic Medical Sonographer
- Obstetric and Gynecologic Sonographer
- Ultrasound Technologist
- Sonography Technician
- Pediatric Sonographer
- Abdominal Sonographer
A career in Sonography is for you if:
- Interested in Ultrasound technology and imaging
- Enjoys working in fields like obstetrics and gynecology or cardiovascular healthcare
- Prefers non-invasive imaging techniques
- Detail-oriented and skilled at interpreting complex images
A career in Songraphy is not a great fit if:
- Uncomfortable with performing intimate exams or working in sensitive medical situations
- Prefers a career with more predictable work hours and patient cases
- Not interested in continuous professional development and staying updated on technological advancements
- Have difficulty interpreting medical images or working collaboratively with other healthcare workers
The Future of Radiography and Sonography

Driven by technological progress, advancements in radiography and Sonography are reshaping the future of diagnostic medical imaging. Images are better enhanced and efficiently interpreted with the use of Artificial Intelligence (AI), while better 3D and 4D imaging techniques provide detailed information for precise diagnosis.
Additionally, Point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) is gaining traction in the medical industry, particularly for its bedside use and quick results. With the introduction of telemedicine, imaging technologies are also expanding to home services and portable machines. These trends highlight the pivotal role of radiographers and sonographers in advancing healthcare delivery through innovation and improved patient care.
Conclusion
Radiography and Sonography offer rewarding career paths in radiologic technology. Each specialization has unique applications and demands a certain set of skills. Whether you’re drawn to X-ray imaging in radiography or the non-invasive nature of ultrasound in Sonography, both specializations play integral roles in diagnosing and treating patients across various medical disciplines.
Choosing between these two fields depends on your interests, strengths, and career goals within the field of healthcare. As the medical imaging industry continues to evolve, it’s important to choose the best trade schools online to gain expertise and stay on top of innovations in these fields.

